Can Ocular Migraine Cause Fatigue?
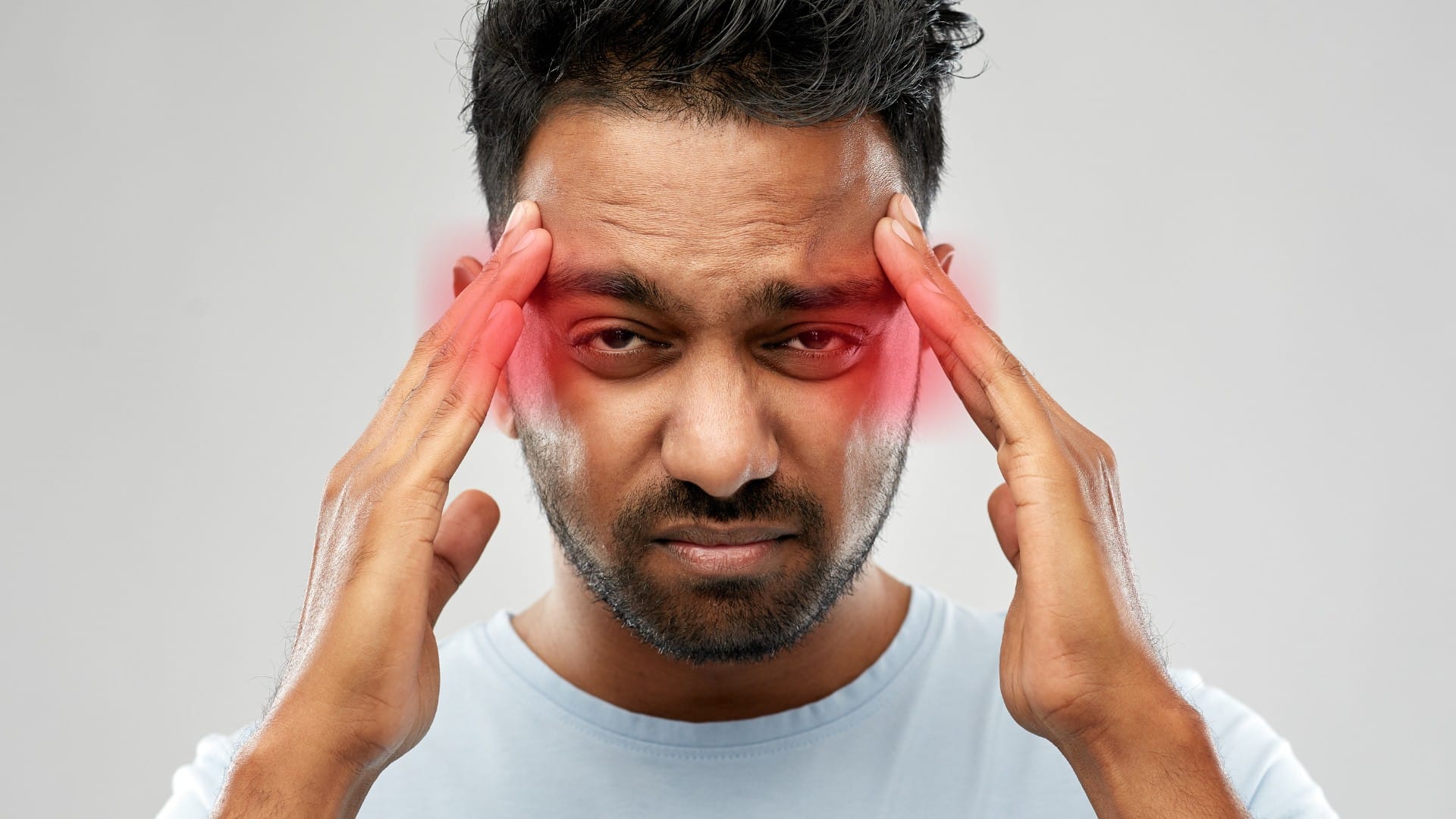
You’re in the middle of a typical day when a shimmering arc of light suddenly appears in your vision. It flickers, grows, and makes it difficult to focus. For many people, this is the beginning of an ocular migraine, a specific subtype of migraine where the visual disturbance often happens without a headache.
ANF Therapy® is an advanced therapy that works on the principles of frequency medicine. It aims to support the body’s natural healing process and restore neurological balance. This therapy utilises frequency-charged, small, circular ANF Devices that are applied to various body areas. They get activated from body heat.
Let’s explore how ocular migraines cause fatigue and how to manage them effectively.
What Happens to Your Body During an Ocular Migraine?
Ocular migraines (also called retinal migraines) involve temporary visual symptoms in one eye. These typically last less than an hour and are caused by either reduced blood flow to the retina or cortical spreading depression, a wave of abnormal activity that spreads across the brain’s visual cortex. While the symptom is limited to your sight, the changes inside your nervous system can ripple far beyond your eye.
During an episode, your brain experiences changes in electrical activity, blood flow, and chemical balance. This “neurological storm” triggers inflammatory changes, alters neurotransmitter levels, and can impact how your body utilises energy. So, even without a headache, your body works hard to restore balance. That’s part of why you can feel so tired afterwards.

What Are the Stages of Ocular Migraine?
While not everyone experiences all phases, the typical progression of an ocular migraine involves several stages.
Prodrome
These early signs can start hours or days before the visual aura. You might feel:
- Mood changes
- Food cravings
- Neck stiffness
- Yawning
- Trouble focusing
Aura
This is when you experience visual symptoms, such as flickering lights, zigzag lines, or temporary blind spots, typically in one eye. It lasts 10 to 60 minutes. It’s the most noticeable part of an ocular migraine, and for some people, it’s the only symptom.
Aura is anxiety-provoking, and the brain may remain on “high alert” for hours. Getting overstimulated after an episode can prevent you from falling asleep or reaching deep, restorative sleep.
Headache
Unlike other migraines, ocular migraines may not include a headache. However, some people do develop a mild or moderate headache after the aura phase.
Postdrome
A postdrome or recovery phase is when fatigue hits the hardest. You may feel drained, foggy, or unwell for hours or even days. This is often called the “migraine hangover.”

What Are the After-Effects of an Ocular Migraine?
Although the visual aura is brief, its impact can linger. Many people experience a postdrome phase, during which the brain and body recover from the event. You might notice:
- Fatigue or a drained feeling, like all your energy got used up.
- Brain fog or trouble concentrating can make even simple tasks feel more challenging.
- Mild nausea
- Sensitivity to light or sound
- Mood shifts, including irritability or sadness
These effects are believed to result from shifts in neurotransmitters (especially serotonin and dopamine), temporary inflammation, and the body’s efforts to restore balance.
How Can an Ocular Migraine Cause Fatigue?
Your brain is one of the most energy-dependent organs. It requires more blood flow than any other organ. During an ocular migraine, it uses extra resources to maintain function. This is a result of several changes.
Neuroinflammation
During a migraine, inflammatory chemicals like CGRP are released. These chemicals can cause you to feel unwell even after the main event, particularly when inflammation affects more than just the visual system.
Energy Depletion
Cortical spreading depression and other brain activity changes consume a lot of energy. Your brain may draw energy from your body’s reserves, leaving you tired and weak afterwards.
Hormonal Imbalance
Your stress hormone cortisol and “feel-good” hormone serotonin fluctuate during a migraine. These imbalances can lower your energy and impact your mood, contributing to feelings of fatigue.
Stress Response
Your autonomic nervous system controls your fight-or-flight response. It may stay activated for hours, leading to a drained, overworked feeling even if you rest during the migraine.
Can Ocular Migraines Cause Body Fatigue?
Yes, ocular migraines can cause both body fatigue and brain fatigue. While ocular migraines start in the eye or the brain’s visual centres, their effects aren’t limited to these areas. You might experience physical symptoms after an episode, like:
- Muscle weakness, especially if it’s in your arms and legs
- A feeling of heaviness in your body, as if gravity increased
- General malaise, or the sense that your body is “off”
- Reduced motivation or ability to do everyday activities
This lack of rest only adds to your fatigue the next day. Moreover, having a fight or flight mode can increase your heart rate, tighten your muscles, and keep your body tense even after the visual symptoms fade. Once that state fades, you’re left with a tired and aching body.

What Does Fatigue From an Ocular Migraine Feel Like?
58.8% of individuals with migraine experience fatigue, which has been attributed to factors like headache intensity, age, and past mental health issues. Every person’s experience is a little different, but many patients describe sensations like:
- You feel like you’ve run a marathon, but haven’t moved.
- Your arms and legs feel heavy or sluggish.
- Every day tasks seem harder, such as walking upstairs or concentrating on a conversation.
- You feel mentally slow, struggling to find words or keep up with your thoughts.
- You may feel emotionally off, more irritable, anxious, or down than you usually do.
How to manage ocular migraine?
ANF Therapy® is a chemical-free, non-invasive treatment approach based on Einstein’s concept of frequency medicine. This therapy uses ANF Devices, which are made of carbonised metal. ANF Therapy® aims to support the body’s healing mechanisms and restore balance in the neurological system, which helps reduce pain and inflammation. It aims not only to address symptoms but also to target the root cause.
According to a real-world study involving 1,054 patients across 45 countries, pain levels decreased significantly, from 7.6 to 3.1 out of 10, when treated with ANF Therapy® . Approximately 92% of patients were satisfied with the results.
Start your journey with ANF Therapy® :
ANF Therapy® is a frequency-based advanced therapy. If you are experiencing ocular migraine symptoms, consult an ANF Practitioner or find an ANF Therapist at www.anftherapy.com/find-clinic to discuss how ANF Therapy® can help you. This drug-free approach aims to address pain and inflammation at its root cause to provide lasting results.
If you’re a healthcare practitioner and want to enhance your clinical skills with frequency medicine, learn more about the ANF Clinical education program by visiting www.anfacademy.com.
Conclusion:
Ocular migraines may seem minor due to the absence of head pain, but they can have a significant effect on both the brain and body, often leading to profound fatigue, brain fog, and physical weakness. This occurs because the brain undergoes intense neurological and chemical changes that deplete energy and trigger the stress response. ANF Therapy® offers a drug-free solution that aims to support the body’s natural healing process and target the root causes of inflammation and imbalance. If you are struggling with recurrent ocular migraines and lingering fatigue, find an ANF Therapist to discuss how ANF Therapy® can help you.